Creating python module in Rust
The objective of the blog post is to implement a python module using the state of art programming language Rust. The idea is to create an python module in Rust.
We will be using the rust-cpython project which makes it possible to execute Python code from Rust and vice-versa build a module in Rust for Python.
Python module
In this section lets create a simple python function for example fibonacci sequence calculator. Follow the steps below to implement this code,
- Create a file named sample_fib.py and copy paste the content below.
#Define a function in python
def fib(n):
#If input is less than 2 return one
if n < 2:
return 1
#Assign the first two values of the series to be one
prev1 = 1
prev2 = 1
#Between the values 1 to the final input
for i in range(1, n):
next = prev1 + prev2
prev2 = prev1
prev1 = next
return prev1
#Execution starts here
if __name__ == '__main__':
print fib(3)
- To run the code,
python sample_fib.py
Rust Implementation
Now lets implement the same python module in Rust and for this we would be using Rust-cpython library, which seamlessly allows the developer to build for Python 2 & 3 with few manipulation in the Cargo.toml file to download the crate.
- Create a new rust projects
cargo new rust_python_fib
We are creating a library in Rust here.
- Enter the new project created:
cd rust_python_fib
- Edit the Cargo.toml file for downloading the cpython dependency.
nano Cargo.toml
The Cargo.toml should look something like this,
[package]
name = "python-rust-example"
version = "0.1.0"
authors = ["Vigneshwer <dvigneshwer@gmail.com>"]
[lib]
name = "example"
crate-type = ["dylib"]
[dependencies.cpython]
git = "https://github.com/dgrunwald/rust-cpython.git"
default-features = false
features = ["python27-sys"]
- Go to ./src/lib.rs and edit the lib.rs file with the code below,
#[macro_use] extern crate cpython;
use cpython::{PyString, Python, PyResult};
//
fn fibo(py: Python, n : u64) -> PyResult<u64> {
if n < 2 {
return Ok(1)
}
let mut prev1 = 1;
let mut prev2 = 1;
for _ in 1..n {
let new = prev1 + prev2;
prev2 = prev1;
prev1 = new;
}
Ok(prev1)
}
// To build a Python compatible module we need an intialiser which expose the public interface
py_module_initializer!(example, initexample, PyInit_example, |py, m| {
// Expose our function fibo as `extern "C"`
try!(m.add(py, "fibo", py_fn!(py, fibo(rand_int: u64))));
// Initialiser s macro needs a Result<> as return value
Ok(())
});
- Compile the project
cd .. && cargo build --release
- Use the project in Python
cp ./target/release/libexample.so ./example.so
python
>>import example
>>print(example.fibo(4))
Benchmarking
Great if you have reached till here, we are almost done. Let’s take a step further to benchmark the performance of the newly create Rust-python module.
- Create a python file and open it in your favourite editor:
touch bench_python.py && subl bench_python.py
- Copy and paster the code snippet below in the python script
#-- #########################
#-- Task: Benchmarking experiments
#-- Author: Vigneshwer.D
#-- Version: 1.0.0
#-- Date: 22 May 17
#-- #########################
# Importing modules
import example
# fibonacci implementation in Rust
def rust_fibo(val):
return example.fibo(val)
# fibonacci implementation in Python
def py_fibo(n):
if n < 2:
return 1
prev1 = 1
prev2 = 1
for i in range(1, n):
next = prev1 + prev2
prev2 = prev1
prev1 = next
return prev1
val =50
# benchmarking rust_fibo
def test_rust_fibo(benchmark):
benchmark(rust_fibo, val)
# benchmarking py_fibo
def test_py_fibo(benchmark):
benchmark(py_fibo, val)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Series value
val =50
# Calling rust version
rust_val = rust_fibo(val)
print "Value predicted by rust_fibo: ", rust_val
# Calling python version
py_val = py_fibo(val)
print "Value predicted by py_fibo: ", py_val
- To run the script:
python bench_python.py
- To benchmark the performance:
pytest bench_python.py
Note:
- To install the pytest framework:
sudo pip install pytest-benchmark
This should give you an output simillar to:
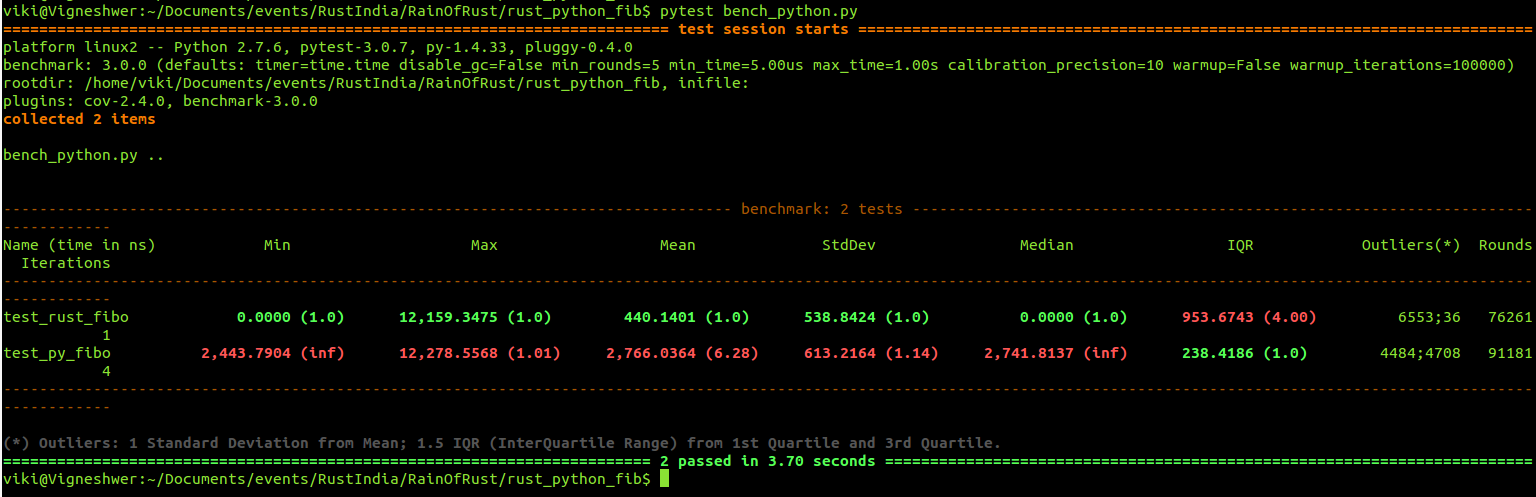
Conclusion
Rust is great language to build python module and has sea of oppurtunities in terms of getting high performance. I am personally excited about building numpy functions in Rust and benchmark them.
Ref: